Assume your company’s standard cost for denim is $3 per yard, but you buy some denim at a bargain price of $2.50 per yard. For each yard of denim purchased, DenimWorks reports a favorable direct materials price variance of $0.50. In order to calculate the direct materials usage (or quantity) variance, we start with the number of acceptable units of products that have been manufactured—also known as the good output. If DenimWorks produces 100 levered vs unlevered cash flow in real estate large aprons and 60 small aprons during January, the production and the finished goods inventory will begin with the cost of the direct materials that should have been used to make those aprons. The direct materials quantity variance should be investigated and used in a way that does not spoil the motivation of workers and supervisors at work place. Variances occur in most of the manufacturing processes and for almost all cost elements.
How is Efficiency Variance Calculated? – A Complete Guide to Efficiency Variance
At the beginning of the period, Brad projected that the standard cost to produce one unit should be $7.35. Per the standard, total variable production costs should have been $1,102,500 (150,000 units x $7.35). Actual variable manufacturing costs incurred were $181,500 over the budgeted or standard amount.
Standard costs variance template
Each output unit should be paid based on the total material costs or wages during the measuring period. To calculate the standard rate, divide the total material costs or salaries paid during the measuring period by the quantity of materials or salaries. In a standard cost system, overhead is applied to the goods based on a standard overhead rate. The standard overhead rate is calculated by dividing budgeted overhead at a given level of production (known as normal capacity) by the level of activity required for that particular level of production. Direct materials price variance account is a contra account that is debited to record the difference between the standard price and actual price of purchase. Let’s assume that the Direct Materials Usage Variance account has a debit balance of $2,000 at the end of the accounting year.
Buttering Popcorn
Here are some situations in which a company should take action to address efficiency variance. There are several types of efficiency variance that a company can experience, each of which provides unique insights into the performance of different aspects of their operations. In this article, we will explore the three main types of efficiency variance in more detail. Furthermore, by continuously monitoring efficiency variance and improving over time, companies can stay ahead of their competitors and maintain a competitive advantage in the marketplace. By reducing efficiency variance, companies can improve their bottom line, increase customer satisfaction, and gain a competitive advantage in their industry. By understanding and analyzing this variance, companies can identify areas where they can improve their processes, reduce waste, and increase profitability.
- This lesser quality denim causes the production to be a bit slower as workers spend additional time working around flaws in the material.
- Figure 8.5 shows the connection between the variable overhead rate variance and variable overhead efficiency variance to total variable overhead cost variance.
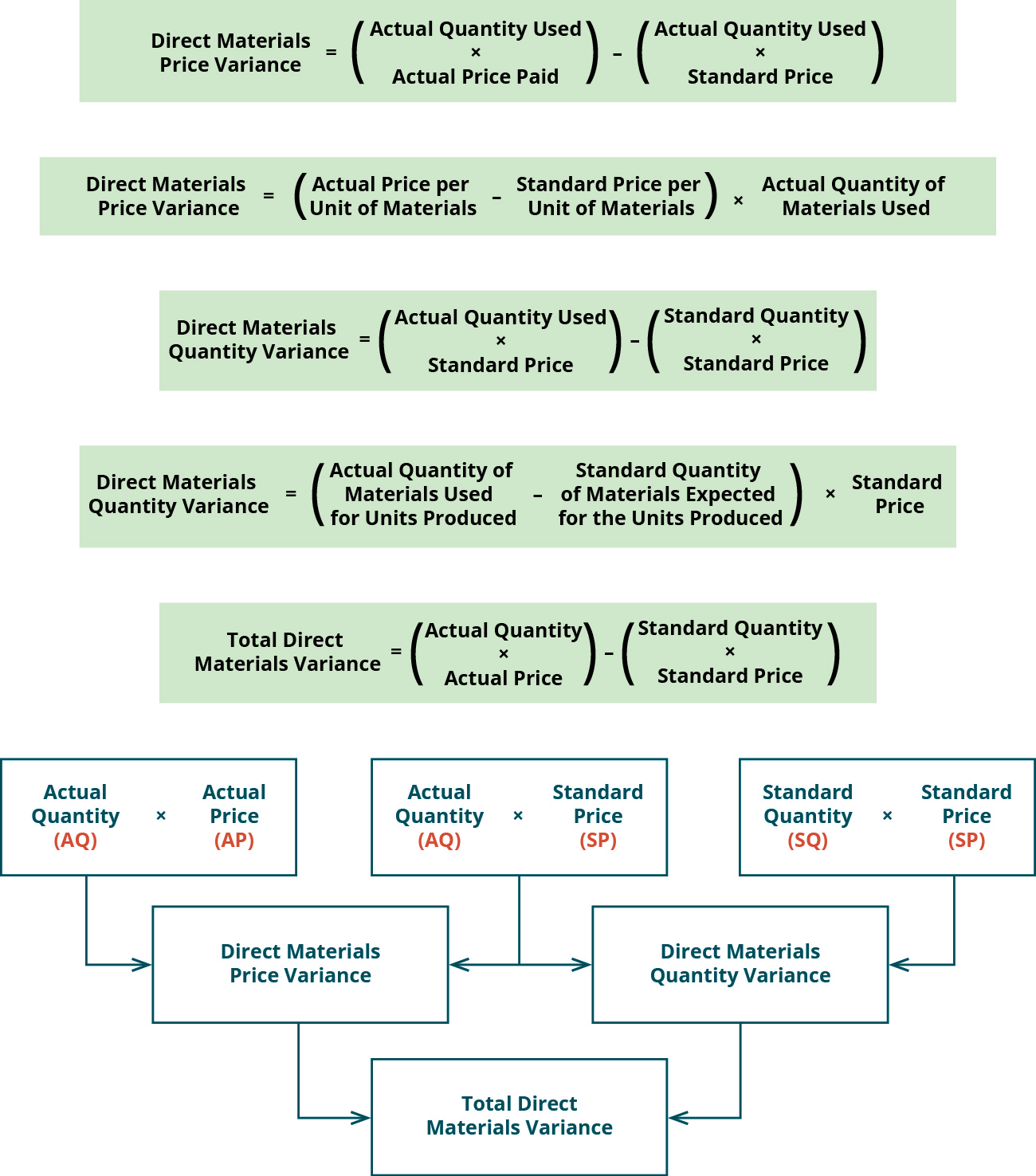
- Using the standard and actual data given for Lastlock and the direct materials variance template, compute the direct materials variances.
- The total direct materials cost variance is also found by combining the direct materials price variance and the direct materials quantity variance.
Variable manufacturing overhead rate variance
Therefore, the total variance for direct materials is separated into the direct materials quantity variance and the direct materials price variance. The template provided in Exhibit 8-3 can be used to compute the total direct material variance, direct material quantity variance, and direct material price variance. The standard and actual amounts for direct materials quantities, prices, and totals are calculated in the top section of the direct materials variance template. All standard cost variances are calculated using the actual production quantity as the cost driver. Let’s assume that you decide to hire an unskilled worker for $9 per hour instead of a skilled worker for the standard cost of $15 per hour.
How confident are you in your long term financial plan?
In this case, the actual price per unit of materials is $6.00, the standard price per unit of materials is $7.00, and the actual quantity purchased is 20 pounds. This is a favorable outcome because the actual price for materials was less than the standard price. With either of these formulas, the actual quantity purchased refers to the actual amount of materials bought during the period. If there is no difference between the standard price and the actual price paid, the outcome will be zero, and no price variance exists. Since direct labor hours are the cost driver for variable manufacturing overhead in this example, the variance is linked to the direct labor hours worked in excess of the standard labor hours allowed.

Ignoring efficiency variance can lead to continued equipment malfunctions and worker injuries, resulting in costly medical bills, workers’ compensation claims, and legal issues. If customers demand higher quality products or faster turnaround times, investing in new equipment may be necessary to meet those demands. Meeting customer demands can improve customer satisfaction and help retain and attract customers. Regular monitoring and analysis of efficiency variance can help identify the root cause of the problem. It is essential to have a system to monitor efficiency variance regularly and analyze the data to identify patterns and trends. This can help to identify areas where improvements can be made to reduce variance and improve efficiency.
Additionally, we have explored when a company should consider investing in new equipment, outsourcing certain processes, and how to ensure that employees are adequately trained to minimize efficiency variance. In today’s digital age, technology is critical in reducing efficiency variance in the manufacturing industry. By leveraging the latest technologies, manufacturers can streamline their processes, improve quality, and increase efficiency, ultimately leading to improved profitability.
These standards are compared to the actual number of direct labor hours worked and the actual rate paid for each type of direct labor. When discussing direct labor, price is referred to as rate, and quantity is referred to as efficiency. Variances between the standard and actual amounts are caused by a difference in efficiency or rate.
